In the context of global sustainable development, combining agriculture with renewable energy has become an important pathway to drive green growth. The agro-PV synergy model, which involves installing photovoltaic (PV) panels above agricultural land, maximizes the three-dimensional use of land resources. This approach not only increases land-use efficiency but also fosters the integration of agriculture with the renewable energy industry, creating new pathways for diversified rural economic development.
Advantages of Agro-PV Synergy
1. Enhancing Land-Use Value
By integrating PV power generation with agricultural production on the same land, agro-PV synergy greatly improves land-use efficiency. Traditional agriculture often uses land solely for crop cultivation or livestock rearing. Agro-PV projects ingeniously place PV panels above farmland, where they don’t interfere with the sunlight and ventilation crops need. Utilizing the previously idle overhead space for power generation maximizes land resources.
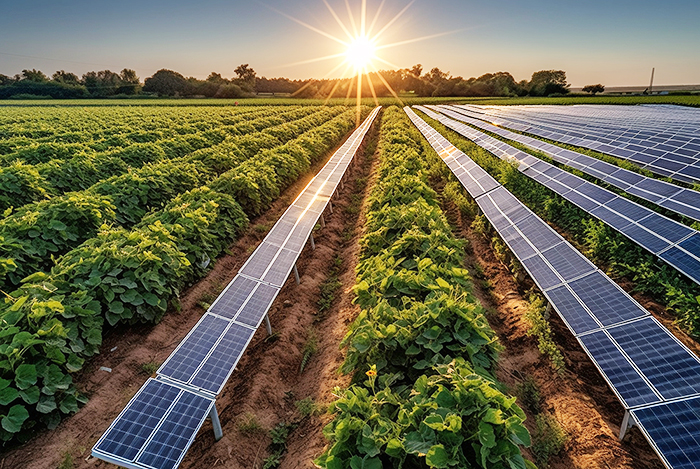

2. Increasing Farmer Income
Agro-PV synergy provides farmers with diversified income streams. Farmers can earn a stable rental income by leasing their land for PV installations. Additionally, the operation and maintenance of PV stations create local employment opportunities, further increasing wage income. Cultivation of shade-tolerant crops beneath PV panels also provides farmers with profitable options, as these crops can thrive under the partial shade provided by the panels.
3. Environmental Protection
This model has significant environmental benefits. Solar power is a clean energy source, and its generation process produces no pollutants, helping reduce fossil fuel reliance and greenhouse gas emissions. PV panels also help lower soil temperatures and reduce water evaporation, improving farmland ecosystems. Furthermore, agro-PV projects promote green farming practices, encouraging farmers to adopt organic cultivation and biological pest control to reduce pesticide and fertilizer usage, thus protecting soil and water resources from pollution.
Applications and Innovations in Agro-PV
1. PV Crop Cultivation
PV crop cultivation installs PV panels atop greenhouses or agricultural structures, utilizing the space below for crop growth. This model optimizes land use while creating a favorable environment with appropriate light and temperature conditions for crops. PV panels can block some UV rays, reduce pest problems, and reflect light to improve crop photosynthesis efficiency. This model suits a variety of vegetables, fruits, and medicinal plants, merging high-efficiency farming with sustainable energy production.
2. PV Livestock Farming
In PV livestock farming, solar power generation is combined with animal husbandry. PV panels can be installed on rooftops or surrounding spaces in livestock farms, supplying clean energy for operations and reducing dependence on traditional energy sources. The shade provided by PV panels creates a cooler, more comfortable environment for livestock, enhancing animal welfare. This approach boosts economic returns for farms and supports green transformation in animal husbandry by lowering carbon emissions.
3. PV Water Management
The PV water management model builds PV stations on water surfaces or reservoirs, integrating PV power generation with water irrigation and pumping systems. The electricity generated drives pumps and irrigation facilities, supplying clean energy for agricultural water management. This model promotes efficient water use and environmental protection. With intelligent control systems, PV power generation and water management can be precisely matched, maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing energy waste.
PV Village Residences
The PV village model integrates solar energy into rural housing by installing PV panels on roofs and courtyards to provide residents with clean electricity. This model not only enhances the energy structure in rural areas, increasing energy self-sufficiency, but also promotes sustainable economic development in rural communities. Combined with initiatives to beautify rural areas, PV villages support an eco-friendly, livable environment, merging PV power with rural environmental improvement and eco-tourism.
PV Ecosystems
PV ecosystems emphasize the harmonious integration of solar power with ecological conservation. With careful planning and management, PV projects can promote ecological restoration, soil conservation, and biodiversity. PV panel areas can be designed to support vegetation recovery and wildlife habitats. PV ecosystems also contribute to sustainable agricultural practices by integrating ecological restoration functions and supporting biodiversity, yielding both environmental and energy benefits.
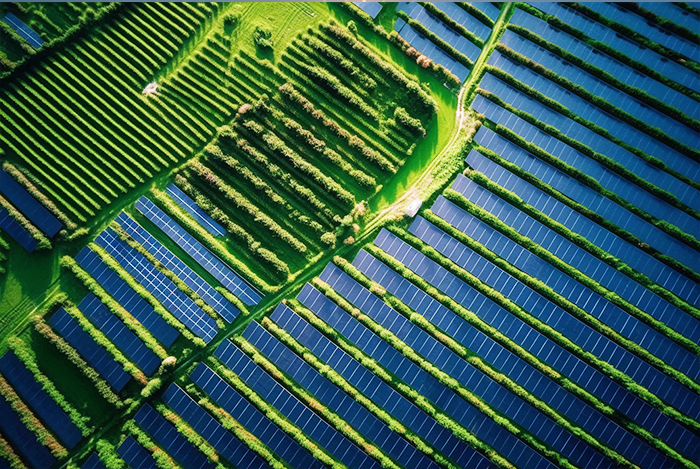

Challenges and Future Prospects
While agro-PV synergy offers numerous advantages, it also faces challenges, such as project implementation, policy ambiguity, high initial costs, and lack of standards. Implementation hurdles include land acquisition, project approval, and interest alignment among stakeholders. Policy ambiguity arises from the dual-use nature of agro-PV, with varied levels of policy support and a lack of uniform regulations. High upfront costs, due to PV equipment, installation, and agricultural infrastructure, make scaling difficult. The lack of unified standards further complicates project consistency and quality.
However, as governments emphasize renewable energy and green agricultural development, policy conditions are improving, cost barriers are gradually decreasing, and the model is poised for significant growth. China’s National Energy Administration actively supports agro-PV and similar models, encouraging policies for sustainable and healthy development in agriculture and PV. Solutions.
In summary, agro-PV synergy maximizes the value of land by integrating solar panels on farmland, with advantages like enhanced land-use value, increased farmer income, and environmental protection. As technology advances and policies mature, agro-PV is expected to play an increasingly vital role in modern agriculture, supporting the goals of agricultural modernization and rural revitalization.