An off-grid solar power system consists of solar panels, a solar charge controller, a battery bank, an off-grid inverter, DC loads, and AC loads. Solar power systems are widely used in remote areas, telecommunications, islands, agriculture, and regions without access to conventional electricity.
During sunlight, the solar array converts solar energy into electricity, which powers the loads through the solar charge controller and charges the battery bank. When sunlight is unavailable, the charge controller directs power from the battery bank to the DC loads. Simultaneously, the battery bank supplies power to the off-grid inverter, which converts DC into AC to power AC loads. Solar power systems are not standardized products, meaning the same configuration may not be suitable for all users. They are designed and configured based on user needs, which vary in different locations. Many customers have limited knowledge of this; therefore, users interested in installing solar power systems may wonder what kind of system they should choose.
1. Pure Lighting or Household Appliances?
Solar power systems can be categorized into two types based on their function:
A solar power system purely for lighting: This is a household DC lighting system.
A system for both lighting and household appliances: This type of system provides 220V AC output to power household appliances. The lighting system is simpler and more cost-effective but cannot power household appliances.
2. Should You Choose a Portable All-in-One System or a Modular System
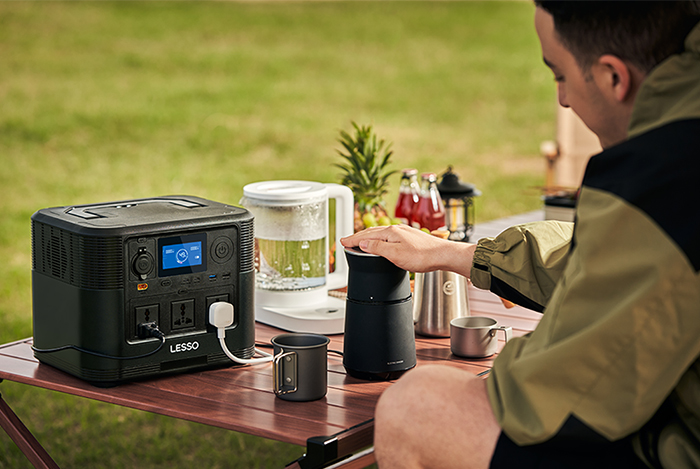

Portable All-in-One Systems: These are designed for easy portability, requiring no installation, and are ideal for outdoor camping. However, due to limited size, they have lower battery capacity.
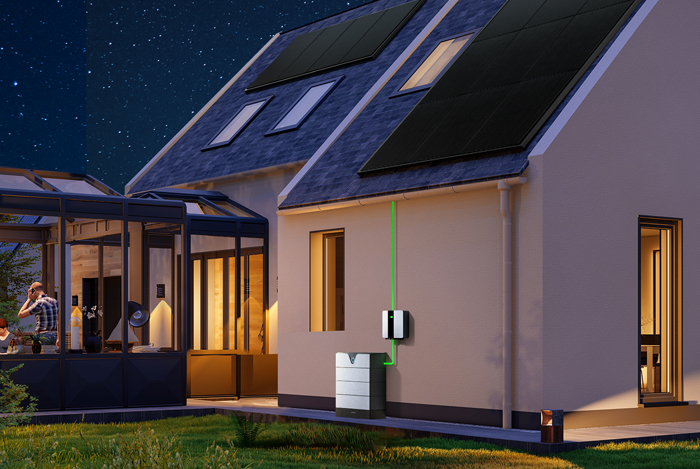

Modular Systems: These require simple installation, offer larger energy storage, and are both practical and cost-effective, making them more suitable for households or outdoor residences. A DC solar power system with a battery bank consists of solar panels, a charge controller, batteries, and DC loads. During sunlight, solar panels convert light into electrical energy to power loads and charge the battery bank. At night or during cloudy weather, the battery bank powers the loads. This type of system is widely used, from solar garden lights and courtyard lamps to mobile communication stations and rural electricity supply in remote areas. When the system size and load power are larger, it will require a solar array and a larger battery bank.
3. AC and DC Solar Power Systems or Hybrid Solar Systems?
AC Solar Power Systems: Compared to DC solar power systems, AC solar power systems include an AC inverter to convert DC into AC to power AC loads.
Hybrid Solar Systems: These systems can power both DC and AC loads.
Grid-Tied Hybrid Solar Systems: These systems prioritize solar power generation with 220V AC grid electricity as supplementary energy. This reduces the necessary size of the solar array and battery bank, as the electricity generated by the solar system can be used immediately on sunny days, while grid power can supplement energy during cloudy or rainy days. In most parts of China, the weather is clear for more than two-thirds of the year, reducing the one-time investment in solar power systems while also significantly contributing to energy savings and emissions reduction.
In summary, off-grid solar power systems can be tailored to different needs, from basic lighting setups to more advanced systems that power household appliances and integrate with grid electricity.