As global energy demand continues to rise and environmental awareness grows, solar energy, a clean and renewable resource, is receiving increasing attention. Rooftop photovoltaic (PV) systems, an effective method of utilizing solar energy, have been widely adopted in many countries and regions. This article explains how rooftop PV systems work, including their main components, the photoelectric conversion process, and energy output.
1. Main Components of a Rooftop PV System
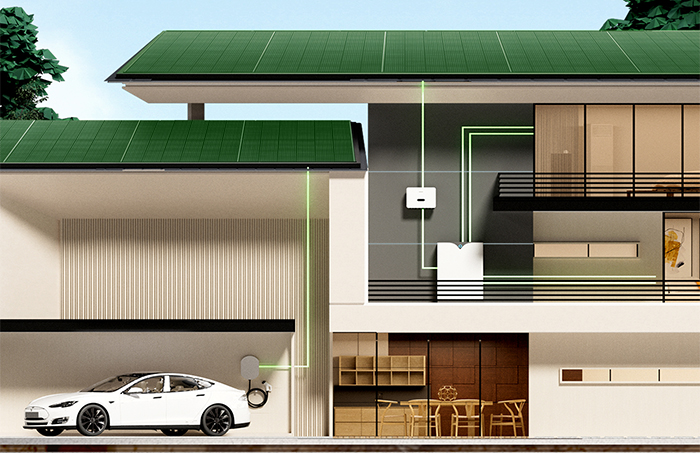
A rooftop PV system consists of several key components, including solar panels (PV modules), an inverter, mounting systems, cables, and a distribution box.
Solar Panels: As the core component of a rooftop PV system, solar panels are made up of multiple solar cells, usually using silicon. Silicon has excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency, allowing sunlight to be converted into electricity. There are three main types of solar panels: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and amorphous silicon. Monocrystalline panels offer the highest efficiency but are relatively more expensive.
Inverter: The inverter’s function is to convert the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use by household or industrial appliances. The inverter's performance directly impacts the efficiency and stability of the PV system, so factors like conversion efficiency, power factor, and reliability should be considered when selecting an inverter.
Mounting System: The mounting system is used to install and secure the solar panels on the roof, allowing adjustments to angle and orientation for maximum sunlight exposure. Types of mounting systems include fixed, tracking, and adjustable mounts, each suitable for different roof structures and needs.
Cables and Distribution Box: Cables connect the solar panels, inverter, and grid, transmitting power. The distribution box protects the PV system, preventing issues such as overcurrent and overvoltage.
2. The Photoelectric Conversion Process in Rooftop PV Systems
The photoelectric conversion process of rooftop PV systems is primarily based on the photovoltaic effect in physics. When sunlight hits the solar panels, photons interact with electrons in the semiconductor material, generating electricity. Here’s how it works:
Photon Absorption: Photons in sunlight are absorbed by the semiconductor material in the solar panel.
Photovoltaic Effect: The energy from photons excites electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to jump from the valence band to the conduction band, creating electron-hole pairs. Free electrons and the holes left behind generate electricity as they move.
Charge Separation and Current Generation: Under the internal electric field of the cell, the generated electrons and holes are separated and move towards opposite ends, creating a voltage difference and generating current.
3. Power Output and Usage
The electricity generated by solar panels is typically in DC form and needs to be converted into AC via the inverter for household or industrial use. In addition, PV systems can store excess electricity in battery packs for later use.
In distributed PV systems, the generated electricity is primarily used by the owner, while any surplus can be sold back to the grid. This “self-consumption with surplus fed into the grid” model not only reduces electricity costs but also contributes to environmental protection.
4. Advantages and Application Prospects of Rooftop PV
Rooftop PV is a clean, pollution-free energy solution with notable advantages. First, solar energy is a renewable resource, ensuring sustainable energy supply. Second, rooftop PV systems integrate seamlessly with buildings, enhancing aesthetics while providing shading and insulation, thereby improving building comfort.
With advancements in PV technology and decreasing costs, rooftop PV systems are seeing wider adoption. In the commercial and industrial sectors, rooftop PV systems offer clean, cost-effective power, reducing energy costs and improving economic benefits. For residential buildings, rooftop PV systems can supply household power, with any surplus sold to the grid for additional income. Additionally, national and local governments strongly support the PV industry, implementing policies to encourage PV installation.
In conclusion, rooftop PV systems operate based on the photovoltaic effect, converting sunlight into electricity via solar panels and supplying it to electrical devices through inverters. As a clean, renewable energy source, rooftop PV offers significant advantages and promising application prospects.