As the global energy structure shifts and clean energy becomes more prominent, solar power plants, a crucial part of green energy, play a significant role in improving energy efficiency and economic benefits. This article explores the basic principles of solar power plants, factors affecting their performance, and measures to increase energy output, offering technical insights for optimizing their operation.
1. Basic Principles of Solar Power Plants
Solar power plants convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic (PV) effect. These plants mainly consist of PV modules, mounts, inverters, distribution boxes, and cables. The PV modules are the core component, converting sunlight into direct current (DC), which is then converted into alternating current (AC) by inverters and either fed into the grid or used directly by consumers.
2. Factors Affecting Power Generation
Several factors impact a solar power plant's energy output:
Sunlight Conditions: The intensity, duration, and spectrum of sunlight are key to PV efficiency. Stronger light and longer exposure result in higher power output.
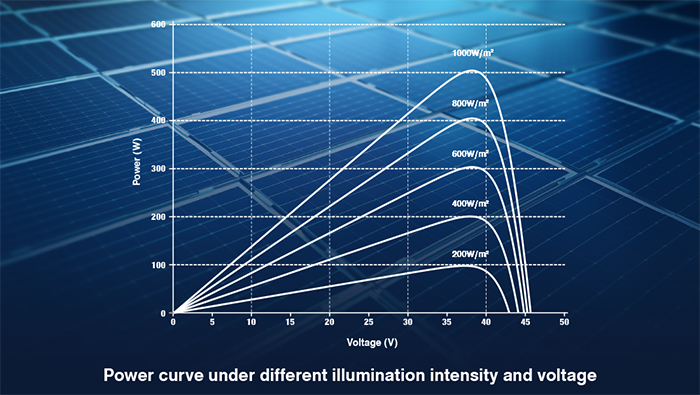
Temperature: Higher temperatures reduce the efficiency of PV modules and inverters, with power output typically dropping by about 0.3% for every degree increase.
PV Module Quality: Efficiency, durability, and resistance to degradation directly influence power output.
Design and Installation: Plant layout, shading, installation angles, and spacing all affect sunlight capture and utilization.
Maintenance: Regular cleaning, fault detection, and equipment updates are critical for stable performance and increased output.
3. Measures to Increase Energy Output
To improve solar plant efficiency, consider these approaches:
Optimizing System Design:
Choose high-efficiency PV modules certified by authoritative bodies.
Design layouts based on local geography and climate to maximize sunlight capture.
Enhancing Power Generation Efficiency:
Lower module temperatures using better cooling systems and optimize ventilation for inverters.
Minimize shading by carefully planning the layout to reduce obstacles that block sunlight.
Improving Maintenance:
Regularly clean PV modules to remove dust and debris.
Maintain and replace faulty equipment promptly.
Install data monitoring systems to track real-time performance and detect issues early.
Adopting New Technologies:
Use solar tracking systems that adjust the panels' angle to follow the sun.
Introduce energy storage systems to ensure power supply during low sunlight or peak demand.
Implement smart management systems using IoT and big data to enhance operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Increasing solar power plant output is a multifaceted process. By optimizing system design, improving efficiency, enhancing maintenance, and adopting new technologies, plants can significantly boost their energy production. However, it’s essential to balance efficiency with cost considerations to achieve the most effective solution for each project.