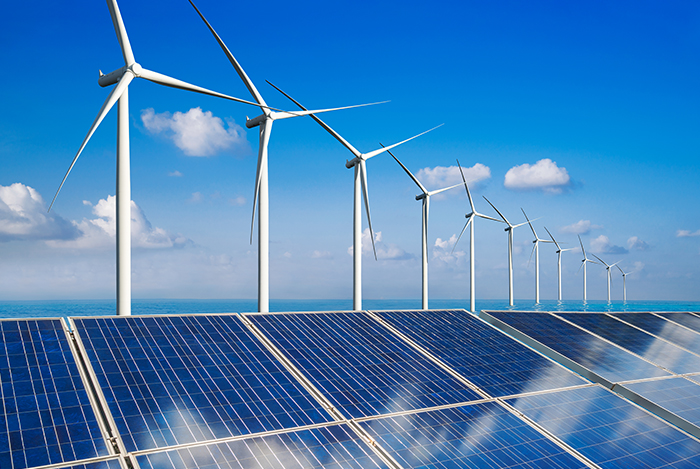
As the problem of global climate change becomes increasingly serious, countries around the world are focusing more on the development of new energy sources. Photovoltaic and wind power, as the two clean energy behemoths, have long played an essential role in the emerging energy landscape. However, photovoltaic and wind power have distinct benefits; who will triumph in the future energy era? Which is a better prospect: photovoltaic electricity generating or wind power generation? This has been the centre of interest in the industry.
I. Market demand and growth potential
With the global need to cut carbon emissions and achieve sustainable development, the demand for photovoltaic and wind power generation has increased dramatically in recent years. Both the PV and wind power businesses have seen exceptional growth, thanks in large part to national legislation.
However, in terms of market demand, photovoltaic power generation appears to have greater potential. Because of its distributed nature, PV power generation may be widely used in residential rooftops, business buildings, agricultural greenhouses, and other fields, expanding the market's application possibilities. Wind power generation, on the other hand, is constrained by geographic location and wind resources, making commercial application scenarios limited.
2. The maturity of technology and innovative capability
In terms of technological maturity, wind power production technology is relatively mature and has been operational for many years, providing the globe with reliable renewable energy. However, solar technology has advanced rapidly in recent years, particularly with improvements in photovoltaic materials, battery efficiency, and energy storage technology, which have considerably boosted the competitiveness of photovoltaic power generation.
Furthermore, the PV business demonstrates significant potential for innovation. The cross-border integration of photovoltaic and energy storage, photovoltaic and hydrogen energy, and other disciplines has opened up limitless opportunities for the solar industry's development. Wind power generation, on the other hand, has seen very few technological advancements, with the primary focus being on improving wind turbine efficiency and reliability.
3. Cost and Return on Investment.
Cost and return on investment are critical elements in determining the viability of new energy projects. In terms of cost, with the continuing development of solar technology and the improvement of the industrial chain, the cost of photovoltaic power generation has been greatly decreased, and it is now approaching or even less expensive than the cost of traditional energy production. At the same time, the cost of wind power generation is falling year after year, while it remains slightly higher than that of PV power generation.
Photovoltaic power generation projects have drawn a significant amount of social capital due to its shorter investment cycle and greater rate of return. Furthermore, photovoltaic power plants have minimal operating and maintenance expenses, which improves their return on investment. Wind power projects, on the other hand, have a longer return on investment cycle, are influenced by policy, geographic location, and other factors, and carry a relatively high level of investment risk.
4. Environmental Adaptability and Social Acceptance
In terms of environmental flexibility, photovoltaic and wind power generation have distinct properties. Photovoltaic power generation requires high sunlight conditions, but effective power generation can be achieved in places with sufficient sunlight; wind power generation is dependent on wind resources and is best suited to wind-rich areas. Both are complementary in terms of environmental flexibility, and they work together to assist the global energy transition.
Photovoltaic power generation is more widely accepted among the general public due to its tiny footprint, low noise, and low visual impact. Wind power projects, on the other hand, frequently necessitate the development of large-scale wind farms in scenic locations, which can have an impact on the local natural environment and landscape, causing public concern and debate.
To summarise, PV and wind power generation offer distinct benefits in terms of market demand, technological maturity, cost and ROI, environmental flexibility, and societal acceptance. Although photovoltaic power generation has higher potential in some ways, wind power generation also plays an important role. As a result, in the future energy period, solar and wind power should not compete, but rather complement each other, collaborate, and contribute to the worldwide achievement of carbon emission reduction and sustainable development targets.