Devices like PV modules (solar modules), inverters, convergence boxes, distribution boxes, racking, and connecting wires make up a PV power plant system. Any issues with one of them may interfere with the regular running of the entire power plant, perhaps leading to significant losses like fire or a loss of power generation.
Based on statistical data, DC equipment failures, including components, inverters, and convergence boxes, account for as much as 90.18% of common PV power station system failures, while AC equipment failures, including cables, transformers, civil engineering, and booster stations, account for 9.82% of these failures.
Typical PV power plant system issues
Quality Issues
1. Issues with the quality of the products and equipment include reconditioned photovoltaic modules, false power labeling, inferior solar panels, severe attenuation; inadequate output power and aging of inverters; incorrect concrete grade and inadequate pouring size; significant mistakes in bracket materials, inadequate zinc galvanizing layer; underwiring of cables and inadequate current-carrying capacity; disorganized use of power distribution equipment, components that don't meet standards, and so forth.
2. Issues with the quality of construction and installation: the primary issues with construction and installation include improper foundation vibration, improper steel cage binding, improper bracket bolt installation node, improper cable connection, poor contact, incorrect connection, improper component installation that results in hidden cracks, and so forth.
Daily oversight
1. Shading: Solar water heaters, structures (walls, chimneys), high-voltage wires, antennae, base stations, railings, trees, weeds, and other objects all provide shade for photovoltaic arrays. Due to the fact that the power output of a PV module can be greatly influenced by only one of its solar cells. The effects of shading that happen most frequently are the corrosion and hot spot effects.
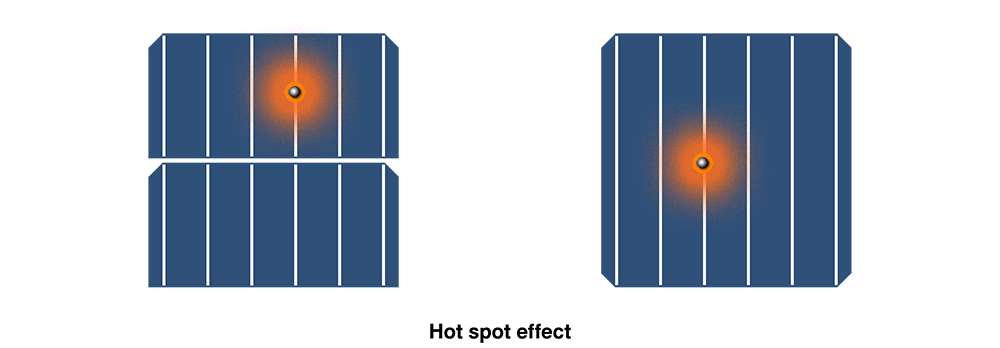
The term "hot spot effect" describes how a PV module's ability to shade a portion of its internal heating much more than a part that is not shaded, making it easier for hot spots to form, which can burn out the module and limit its service life and power generation efficiency;
The term "corrosion effect" refers to the toxic compounds that fall on the surface of solar panels due to dust adsorption from the atmosphere. These substances can be acidic or alkaline, and they can cause the surface to corrode. They can also produce diffuse reflection of sunlight, which lowers power generation.
2. Dust and snow: Particles of dust, such as dust from industrial pollutants, vehicle exhaust, and soil, are suspended in the air. The effectiveness of solar module power generation will be impacted by dust, bird droppings, sand, plant leaves, building splatter stains, oil, and other contaminants that are easily introduced to exterior surfaces where the modules are placed. Similarly, snow falling on a photovoltaic module has the potential to cause shadow masking, which would cut off the generation of PV electricity.
A partially shaded module will have a lower current in the shaded portion of the cell than in the other cells. The "hot spot effect" is caused by the darkened area placing additional strain on the power supply by turning electrical energy into heat and raising temperatures.
Long-term shadowing can result in a constant high temperature in the hot spot area of the module, which can burn out the cell and the junction box or possibly start a fire. Long-term shadowing also causes the shaded part of the cell to act as a load for an extended period of time.
3. Hidden danger management: The operation of a photovoltaic power plant should not overlook hidden dangers such as the use of PV square arrays in the field to construct makeshift homes, firewood piles, carelessly piled weeds, crazy vines and weeds, planting and raising of plants and poultry, hay left in the field untended, graves not promptly moved and thus growing in number, a bird's nest, hornet's nests, cobwebs, and so forth. Ignorance of these hidden risks can easily lead to a decrease in the heat dissipation impact of solar arrays, increase system loss, and lower power generating energy. If insects in the distribution box are not removed promptly, there is a risk of line short circuiting, equipment burnout, higher maintenance costs for the power plant, and decreased revenue from power generation. Particularly in the winter and around the Qingming Festival, there is a high probability that the field's graves, hay piles, and waste may catch fire.