With the national strategy and policy support for new energy sources, the concept of green energy has become deeply ingrained in people's minds. Technological advancements and declining installation costs have led to an increase in the number of people installing solar PV systems on their roofs. Beyond the environmental benefits, many are primarily concerned with the financial returns of household PV systems. This discussion focuses on the factors that influence the revenue from household distributed PV power plants.
Many homeowners with PV systems report that their power generation is not as efficient as expected, often due to deviations from the optimal tilt angle. For instance, in Shanghai (latitude 31 degrees), if PV panels are installed at a 23-degree angle instead of the theoretical optimal 31 degrees, does this significantly reduce efficiency?
The Myth of the Optimal Tilt Angle
The so-called optimal tilt angle, which maximizes solar radiation reception, does affect PV efficiency. However, in practice, it's not the sole determinant. The optimal angle varies dynamically and installation environments differ greatly. Even if installed at the optimal angle, revenues can vary.
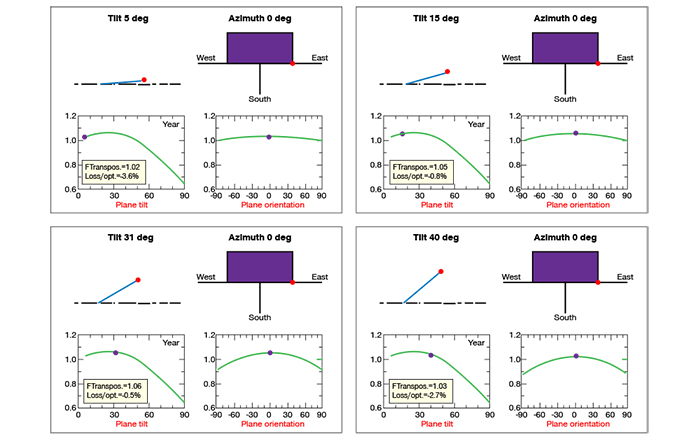
While the tilt angle affects efficiency, its impact is often minor. Installation companies typically choose a suitable angle based on comprehensive considerations. For example, in Shanghai (31 degrees north latitude), simulations show efficiency losses at various angles: 5 degrees (3.6%), 15 degrees (0.8%), 25 degrees (0%), 30 degrees (0.5%), and 40 degrees (2.7%). Thus, angles between 15 and 35 degrees are generally acceptable. Prioritizing a small efficiency gain at the cost of significant site area may reduce overall benefits.
Key Factors Affecting Revenue
Since the tilt angle's impact is minor, other factors play a more significant role in revenue generation.
1. Safety
Safety is paramount; without it, discussing revenue is moot. Home PV systems may be installed on roofs ranging from two to thirty stories high. Poor design can lead to serious safety hazards.
Design Considerations: Pursuing the best tilt angle might require high brackets, which impose significant structural demands on the roof. Structural failures are not uncommon.
Maintenance: Proper maintenance access is crucial. Some installations cover the entire roof, making maintenance difficult. Regular cleaning is essential, as even minor obstructions like bird droppings can significantly affect performance.
2. Shading
The misconception that a little shading won't matter is incorrect. Even minimal shading can cause a 10% loss in efficiency or damage the PV system, directly impacting revenue.
3. Orientation
Most homes are oriented north-south, but many also face east-west, and multi-faceted roofs are common. For optimal revenue, avoid installing panels on the east, west, or north sides. South-facing panels, or those deviating by about 15 degrees, are preferable.
Conclusion
The tilt angle is less critical than commonly believed. Safety, site area utilization, and environmental factors have the most significant impact on revenue. Designing a PV system that considers these factors will maximize returns.