As an important part of photovoltaic power generation, the main role of the inverter is to convert the direct current from photovoltaic modules into alternating current. At present, the common inverter on the market is mainly divided into centralized inverter and group series inverter, and the new-style distributed inverter.

How it works:
· Series inverter: a series of photovoltaic cells into a high-voltage DC input, and then converted to AC output.
· Parallel inverters: multiple photovoltaic cells are connected in parallel to increase the total current, which is then converted to an AC output.
· Bridge inverter: the use of bridge circuit for dc-to-ac conversion.
· Intermediate-frequency inverter: by converting the DC input into intermediate-frequency AC, which is converted in the transformer to obtain the desired AC output.
Based on output waveform:
· Sine wave inverter: the output is a pure sine wave, suitable for power quality requirements of higher applications.
· Modified sinusoidal inverter: the output waveform is a modified sinusoidal waveform, with certain harmonic components cut for most home and commercial applications.
· Square wave inverter: the output waveform is square wave, simple and low cost, but will introduce more harmonics.
· Pulse width modulation (PWM) inverter: the use of high-frequency PWM technology to produce near-sinusoidal output waveform.
Based on areas of application:
· Independent inverter: for independent power generation systems independent of the main power grid, such as lighting, power supply, etc.
· The solar inverter: connect photovoltaic power to the main grid and inject excess power into the grid when it is not needed, and get insufficient power from the grid.
· Micro-grid inverter: micro-grid system can achieve networking and management, will be different power sources (such as solar, wind, etc.) and load connected.
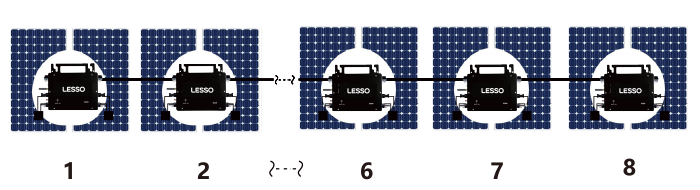
These are some common solar inverter categories. Different types of inverters have different characteristics and applicable scenarios. It is necessary to select the appropriate inverter type according to the specific requirements and application scenarios.
What's the solar inverter for:
The solar inverter is used to convert direct current (DC) generated by photovoltaic panels (solar panels) into alternating current (AC) . Photovoltaic panels convert sunlight into direct current, and solar inverter convert that direct current into the alternating current we normally use to power homes, industry and business.
The main roles of solar inverter are as follows:
1. Power Conversion: the solar panel output of DC into AC power to meet the needs of the power grid. Alternating current (AC) is the form of electrical energy used in our daily life and industrial production.
2. Grid-connected: for photovoltaic systems connected to the grid, the solar inverter can inject excess power into the grid to reduce dependence on the grid and generate a certain amount of online revenue.
3. Power management: the solar inverter is usually able to monitor and manage the PV system, monitoring the status, current, voltage, etc. of the PV panel in real time, to provide users with the ability to monitor and optimize the performance of PV systems.
4. Protection Functions: the solar inverter usually have overload protection, short circuit protection, overvoltage protection, undervoltage protection, etc. to ensure the safe operation of the PV system.
In short, solar inverter plays a crucial role in photovoltaic systems, converting light energy into useful alternating current, allowing solar energy to be used for power supply and grid access, to achieve sustainable development and energy conservation and emission reduction goals.
The main raw materials of inverter include the following categories:
1. Semiconductor device: the key component of the inverter is the Power semiconductor device, usually using a power Transistor (IGBT) or a Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) . These devices are used to convert electrical energy from DC to AC.
2. Capacitors and inductors: capacitors and inductors are also used in inverters to store and filter electrical energy. Capacitors smooth the output voltage and current, while inductors filter out high-frequency noise and harmonics.
3. Heat sink and heat sink material: The Power Device in the inverter will produce a lot of heat, need heat sink and heat sink material to effectively reduce the temperature, ensure the normal operation of the device. Radiators are usually made of aluminum or copper to provide adequate cooling area.
4. PCB (Printed Circuit Board) : PCB is the carrier for the installation and connection of electronic components in the inverter, with good electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. The inverter circuit design will be based on the power requirements and circuit layout for the corresponding wiring and connection.
5. Electronic component and circuit components: the inverter also needs to use a variety of circuit components, such as diodes, resistors, transformers, fuses, connectors, etc. for circuit control, protection and connection.
In addition, the case of the inverter is usually made of metal materials, such as aluminum alloy or steel plate, used to provide good mechanical protection and heat dissipation performance.
These are the main raw materials of the inverter, these materials in the inverter design and manufacture play an important role in ensuring the performance and reliability of the inverter.