A ground-mounted solar power plant is one of the key applications of modern solar power technology, playing an important role in driving the global energy transition. As the demand for renewable energy continues to grow, these solar plants, with their large-scale power generation capacity and cost-effectiveness, have become a top choice for clean energy development worldwide.
Ground-mounted solar power plants consist of solar panels installed on the ground, converting sunlight into electricity. These large-scale solar projects often feature hundreds or even thousands of solar panels that harness solar energy through the photovoltaic effect. The generated electricity is then fed into the grid for industrial, commercial, or residential use. Due to their size, ground-mounted solar plants require significant land areas and come with specific technical requirements to ensure efficient operation.
Six Key Advantages of Ground-Mounted Solar Power Plants
1. Large-Scale Power Generation
One of the most notable advantages of ground-mounted solar plants is their ability to generate electricity on a massive scale. Unlike rooftop or small distributed solar systems, these plants can accommodate a larger number of panels, generating substantial power to meet the energy needs of industries and households alike. Many large ground-mounted solar plants have become key sources of electricity for regional or national grids.
2. Flexible Layout
Ground-mounted solar plants offer flexibility in design and layout. The system can be adjusted based on various land conditions to optimize the use of solar resources. With adjustable solar mounts, panels can be positioned at the optimal angle to capture maximum sunlight. This flexibility ensures high efficiency even in areas with complex terrain, making these plants adaptable to various environments.
3. Broad Applicability
These solar plants can be installed on different types of land, including barren land, abandoned industrial sites, or agricultural fields. As long as there is sufficient sunlight and space, solar plants can be built almost anywhere. Especially on land that is unsuitable for farming or other uses, solar plants can provide economic value, reducing competition for arable land.
4. Easy Maintenance
Compared to rooftop systems, ground-mounted solar plants are easier to maintain. Since the panels are ground-mounted, technicians can easily access them for cleaning, inspections, and repairs. Regular cleaning is essential to prevent dust and debris from affecting efficiency. The ground installation makes these tasks more convenient and reduces maintenance costs.
5. Economic Benefits
As technology advances, the cost of solar power has significantly decreased in recent years. Ground-mounted solar plants have lower construction and maintenance costs compared to other renewable energy projects, offering a shorter return on investment. Additionally, these plants can create local jobs and promote economic growth. Many countries offer incentives like subsidies and tax breaks to encourage the development of such projects.
6. Sustainable Development
Solar power is a clean energy source that produces no greenhouse gas emissions or pollutants. Ground-mounted solar plants help reduce dependence on fossil fuels, lowering carbon emissions and addressing global climate change. As more countries set carbon neutrality targets, these plants will play a vital role in promoting sustainable development.
The Future of Ground-Mounted Solar Power Plants
As the global demand for clean energy grows, ground-mounted solar plants have a bright future. Countries like China, the U.S., and Germany are heavily investing in solar projects to reduce fossil fuel dependence and lower carbon emissions. In regions with abundant sunlight, such as the Middle East, Africa, and Australia, there is significant potential for large-scale solar plant development.
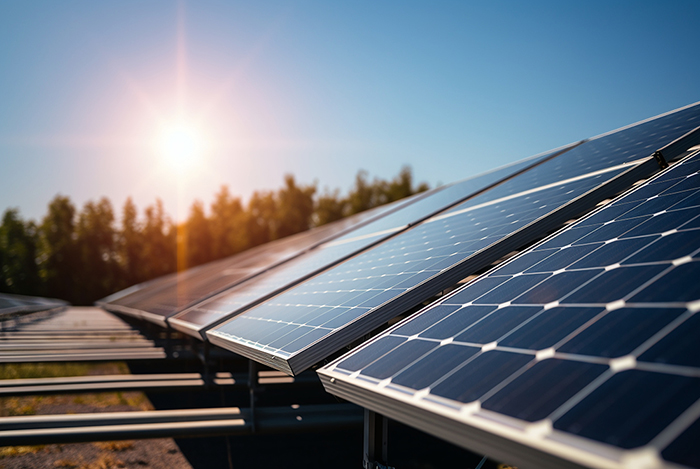

In the future, as energy storage technologies advance and solar plants integrate with other renewable energy systems, ground-mounted solar power plants will become an even more central component of the energy landscape. With ongoing technological progress, these plants will continue to contribute to the growth of clean energy for decades to come.